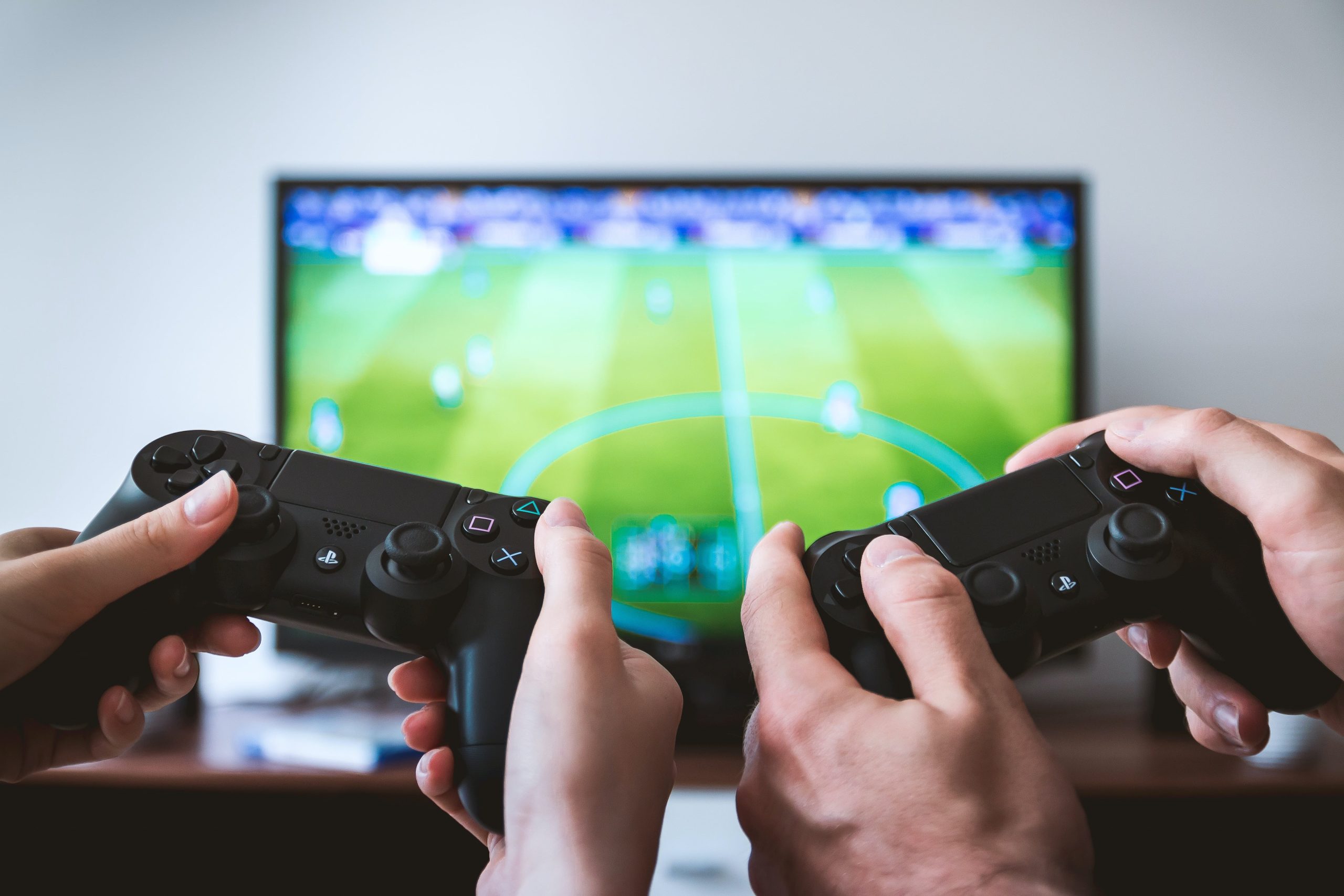
Struggling with a high broadband latency can be incredibly frustrating.
If your latency is high, you will likely experience lag when playing video games, as well as a poor experience on video calls, if the problem is bad enough.
In this guide, we’ve explained seven steps you can take to reduce your ping, which is a measure of your broadband connection’s latency.
Broadband latency explained
Before we look at how to fix your latency, it’s important to understand what causes high latency, so that you can get to the bottom of the issue.
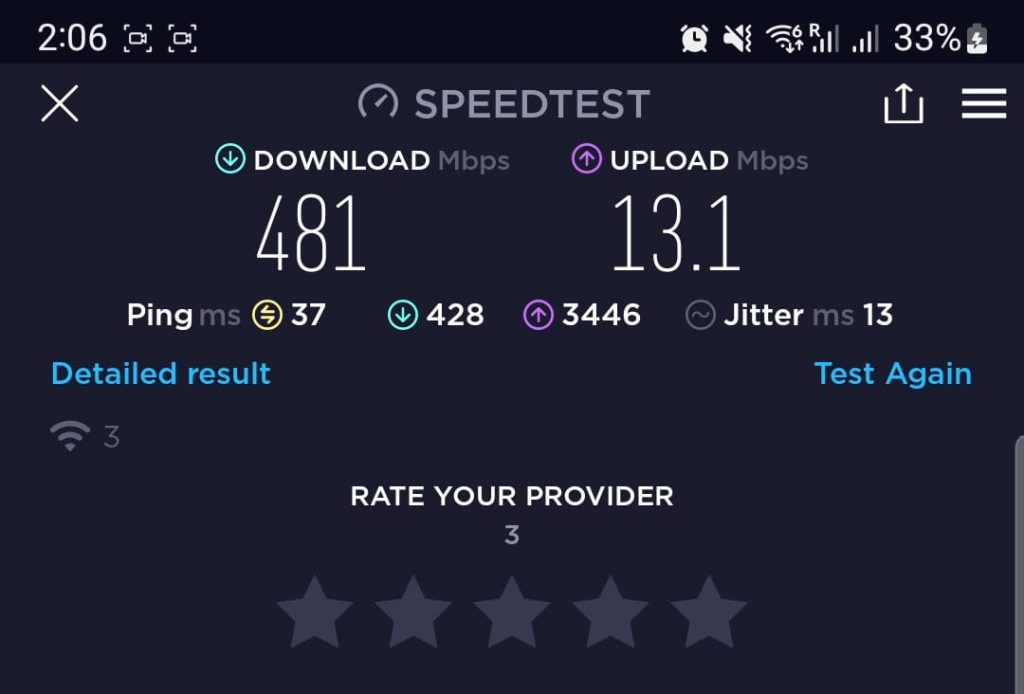
While your broadband speed measures how fast you can download or upload data, ping measures the responsiveness of your connection – how quickly you can send/receive very small packets of data.
When doing data-intensive activities, such as streaming Netflix, your download speed is the most important thing. However, for other activities where there is a constant stream of small data packets being sent and received, such as when online gaming, your latency is much more important.
With a low latency of 10-30 milliseconds, you won’t notice any delay between data packets being sent and received. However, having a high latency (more than 100 milliseconds or so) introduces a noticeable lag between the data being sent and received.
Latency is made worse by:
- Using Wi-Fi instead of a wired Ethernet connection.
- Your broadband connection being overwhelmed, given the amount of bandwidth available.
- Having to communicate with servers on the other side of the world. This is why when online gaming, you normally connect to local game servers. It’s also why you notice a delay when having a Zoom call with someone on another continent.
How to reduce broadband latency

Below, we’ve explained how to reduce your broadband latency
We’ve ordered these fixes based on their likely effectiveness, and how easy they are to implement.
1. Restart your router
When troubleshooting latency issues, the simplest fixes are always worth trying first.
By restarting your router, you’ll clear its temporary memory, as well as its network settings. This can help to fix latency issues, especially if it’s been a long time since you last restarted your router.
To restart your router, unplug its power connection, wait at least 15 seconds, and then plug it back in again. At this stage, you may need to press the power button on your router in order to reboot it, unless the device restarts automatically.
2. Stop using Wi-Fi

Although this isn’t always possible, one of the best ways to reduce your latency is to stop using Wi-Fi as much as possible.
By plugging your devices into the router directly using an Ethernet cable, you’ll make it much faster for small packets of data to reach your computer or games console, reducing your ping significantly, as well as improving your download speeds.
It’s important to note, switching away from Wi-Fi isn’t possible on mobile phones, small laptops, and handheld games consoles, like the Nintendo Switch. Also, running a cable directly to your router might be a bit cumbersome.
However, if your computer is located a long way away from your router, you can use something called a powerline adapter to avoid having to run a cable directly.
Using a powerline adapter, you’ll be able to send internet signal along your home’s electricity cables, making it much easier to get a wired internet connection set up on your Xbox, Playstation, gaming PC, or any other devices with an Ethernet port.
3. Get better Wi-Fi signal
If it’s not possible to avoid using Wi-Fi, you need to be doing everything you can to improve your signal if you want to reduce your latency.
To see if this issue is causing high latency, try to perform a speed test over an Ethernet connection. If your ping improves, the issue is likely caused by poor Wi-Fi signal.
Here are some things you can do to improve your Wi-Fi signal:
- Move closer to your Wi-Fi router.
- Switch from the 5.0 GHz network broadcast by your router to the 2.4 GHz network, which offers better signal over longer distances.
- Use a mesh Wi-Fi system to get better Wi-Fi coverage if you have a large house.
- Avoid placing any devices that could cause interference near your router, such as baby monitors or microwave ovens.
- Avoid enclosing your Wi-Fi router, such as by putting it in a cupboard.
4. Turn off your VPN

While using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) can help to improve your privacy online, using these services is also a certain way to increase your latency as well.
VPNs redirect your internet traffic through another country, and sometimes multiple different countries. This takes time, which introduces latency.
Try to turn off your VPN, and see if this reduces your latency. Or if you can’t turn off your VPN, try to connect to the closest-possible location, to minimise the extra distance that your data packets have to travel.
5. Reduce network usage
Another common reason for high latency, whether you’re using Wi-Fi or not, is that your broadband connection is overwhelmed.
When too much data is being requested on the network at any given moment, relative to the download speed you have, your broadband connection won’t be able to cope. This will lead to slow download speeds and a high latency.
This issue is most likely to occur if you have a relatively slow broadband connection, with a download speed of 50-75 Mbit/s or less, and it’s common for multiple people to get online at the same time.
To fix this issue, you can either limit the amount of people getting online at once, or you can upgrade to a faster broadband plan. Read our guide to learn how much download speed you need, given the number of people at home, to see if it would make sense to upgrade your broadband connection.
6. Use fixed instead of mobile broadband

While mobile broadband is becoming increasingly popular, thanks to the speeds offered by 5G, it doesn’t offer as low a latency as you’ll get with a fibre broadband connection.
To minimise your ping, it’s best to switch to fixed broadband, if possible.
If you need to keep using mobile broadband to get online at home, try to use Ethernet as much as possible. Also consider installing external antennas on your router, in order to get better mobile network signal.
7. Set up quality of service (QoS) rules
This is a bit of an advanced technique, but if you’re struggling with high latency due to a lack of bandwidth, and you can’t upgrade to a faster broadband connection, you might be able to fix the issue using quality of service (QoS) rules.
QoS settings tell your router how to prioritise different types of internet traffic. You can use them to give certain devices on your network, or certain applications, specific amounts of bandwidth that they are entitled to. You’ll be able to prioritise traffic that matters more to you, such as connections to game servers.
To set up QoS rules, you will need to log into your router’s settings. From here, the process depends on which router you’re using. On some routers, you’ll only be able to prioritise traffic by device or MAC Address, while other routers will allow you to prioritise traffic by application, or type of traffic, as well.

I’m Roger, and I’m the founder of Broadband 4 Europe.
I grew up in Switzerland but live in Germany now, and also lived in South Tirol for a while in the past.
I have a background in IT and have performed extensive research into the broadband markets of most major European countries. Learning about fixed-line broadband markets is my nerdy hobby, but I’m also excited by the possibilities that 5G (and eventually 6G) broadband will provide us in the future.
When I’m not researching broadband companies and their networks, you’ll find me playing volleyball or the piano.